Background
Earlier, computers were merely used for storing records. But now, they have become a backbone of the decision-making process of a business. We know that the use of technology has made business more efficient. Yet, we cannot undermine the fact that the associated risks have also evolved with the evolution of technology. This emphasizes the need to implement internal controls in the IT infrastructure of business to avoid/mitigate/reduce/accept risks. Normally, people focus on human-prone manual risks. But they tend to ignore the IT infrastructure level risks, some of which even a person with limited knowledge can exploit.
This article discusses wide array of subjects including some practical scenarios of fraud in an IT infrastructure, influence of COVID-19 towards digitization, importance of risk assessment and IT System’s Audit. The language of the article is kept simple for general audience to relate and understand.
Scenarios
Let us assume different scenarios wherein a fraudster, say Mr. Fraud, could try and circumvent the IT infrastructure. We will also discuss a potential solution that an entity could implement to counter Mr. Fraud’s notorious intentions.
Assume Mr. Fraud has recently joined the purchase department of Victim Company. He, out of his old die-hard habits, decides to fiddles around with the existing IT controls.
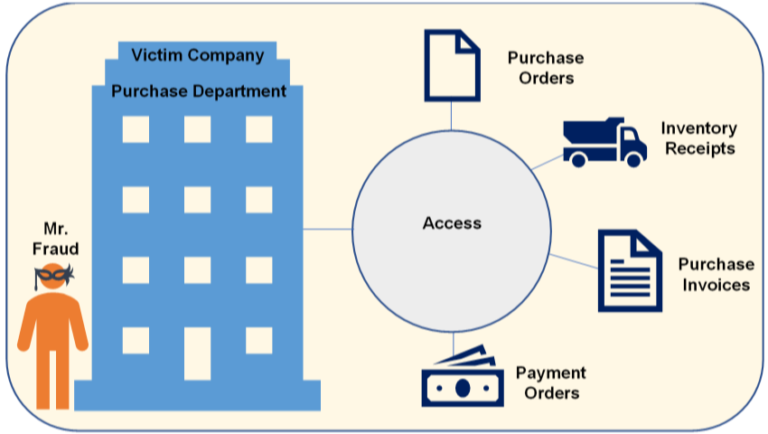
#
Attempts
Potential Solutions
1
Mr. Fraud realises that he is able to access the vendor master. Also, he is able to create and modify records in the vendor master. Mr. Fraud creates a fictitious vendor ‘The Fraud Enterprises’ in the system.
Restrict access of vendor master to authorized personnel only.
Segregate duties of people based on access to create/modify a vendor.
Additionally, implement a maker-checker control whereby another person has to approve the vendor. A maker-checker control is a control where a different person has to approve a transaction performed by one person to process.
2
Let’s assume a case where Mr. Fraud could not create a vendor but was able to create a purchase order for ‘The Fraud Enterprises’. The system allowed creating purchase orders for suppliers not defined in the vendor master.
Restrict purchases, receipts and invoices to suppliers defined in the vendor master and for goods and services defined in the item master.
Additionally, restrict creating/modifying purchase orders for value of goods and services above the rates defined in the item master.
3
Mr. Fraud makes an under the table deal with a supplier – Mr. Opportunist and creates a fictitious purchase order in his name.
Restrict access of transactions to create/modify purchase orders to authorized personnel only.
4
Mr. Fraud performs a fictitious inventory receipt from Mr. Opportunist.
Map Goods Receipt transactions with open Purchase Orders to restrict over-receipt of goods.
Segregate duties of people who have access to create/modify Purchase Orders and people who have access to create/modify Inventory Receipts.
Define an upper tolerance limit for restricting receipt of goods above a certain level from the quantity mentioned in the respective purchase order.
5
Mr. Fraud books a fictitious purchase invoice from Mr. Opportunist.
Map Purchase Invoice transactions with un-booked goods receipts and open Purchase Orders to restrict over invoicing at quantity and amount level.
Segregate duties of people who have access to create/modify Purchase Orders, people who have access to create/modify Inventory Receipts and people who have access to create/modify Invoices.
6
Mr. Fraud books a fictitious purchase invoice from Mr. Opportunist and makes a payment order.
Restrict access of payment orders to authorized personnel only.
Segregate duties of people with access to create/modify invoice and people with access to create/modify payment orders.
Additionally, implement a maker-checker control where another person has to approve the payment order.
The above instances are simply illustrative and the scope of the fraud and controls are extremely broad. We have just seen the tip of the giant iceberg hidden underneath the sea.
The controls discussed in the above illustrations are known as application controls. It includes completeness and validity checks, identification, authentication, authorization, input controls, and forensic controls, among others.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
The situation created by the COVID-19 pandemic has been an eye-opener for many business entities. And, by now, they must have realized the importance of digitization. It is time for people who were averse of technology to embrace it but with caution. A strong IT Infrastructure is definitely a roadmap to a very successful future. A question which everyone should ponder is – What is your strategy during the crisis, right after the crisis and for the new normal?
Need of the hour
Embracing new technology is the roadmap to transform business models, drive growth and improve efficiency. The business processes and controls, though efficient and effective today, may be completely obsolete tomorrow.
Yet, we must also realize the risks which come along with digitization, as discussed earlier. But, one can avoid many risks simply by implementing commonly known best-practices. To survive and thrive, learning from the past while looking at the future should form the base of risk management. The risk assessment should include all categories of risk and should be enterprise-wide. Additionally, in light of the face past change of technology, one must update the controls regularly as well.

Conclusion
It has become incumbent for business to ensure security of their IT infrastructures and ensure the confidentiality, integrity and availability of the application and its associated data.
This has increased the importance of IT System’s Audit. The role of an IT auditor is unknown to most but it impacts the lives of all. It adds security, reliability and accuracy to the IT infrastructure of the business. The role of an IT auditor is extremely dynamic which includes identifying the weakness in the IT infrastructure and creating an action plans to prevent the threats before they materialize.
The need for audit of Information Systems can be highlighted as under:
- High Cost of Incorrect Decision Making: Management and operational controls taken by managers involve detection, investigations and correction of the processes. An independent third-party review can ensure accurate data to make quality decisions.
- High Cost of Computer Error: In a computerized enterprise environment where many critical business processes are performed through the use of systems, an error in data has a huge potential of disruption.
- High Cost of Uncontrolled Evolution of Technology: Use of technology and reliability of complex computer systems cannot be guaranteed and the consequences of using unreliable systems can be destructive.
- High Cost of Technology Abuse: Unauthorized access to systems, unauthorized physical access to facilities and unauthorized copies of sensitive data can lead to destruction of assets (hardware, software, data, information etc.).
The key benefits of IT Audit can be classified as under:
- Enhanced security of data: It provides the business an opportunity to improve or strengthen poorly designed or ineffective controls.
- Reduced IT Related Risks: It reduces, if not mitigates, the risks of confidentiality, integrity and availability of IT processes and data due to timely assessment.
- Enhanced IT Governance: Compliance with Laws and regulations by the business and its stakeholders should be inherently built in the IT infrastructure. It provides a business an evaluation of how much is it synchronized with law.
Conducting a risk assessment more frequently, ideally on a continuous basis, will go a long way to avoid, reduce or mitigate risks. An IT Auditor can bring the required subject-matter knowledge and business insights to provide an objective assessment of the current state and offer guidance on developing an efficient and effective internal process.
To prepare for tomorrow is not something which can be done overnight but is a journey. Digitization, or should we say Machine over Man, is likely going to be the new normal. Are we ready?
Let’s connect to discuss more.

